Introduction to the Mil Mi-8 (NATO Reporting Name: Hip)
The Mil Mi-8, known to NATO as the “Hip”, stands as one of the most prolific and reliable helicopters in aviation history. Developed by the Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant, this twin-turbine medium transport helicopter made its maiden flight on July 7, 1961, and entered active service in 1967. Designed for both military and civilian applications, the Mi-8 quickly became a cornerstone of aerial mobility for over 50 nations worldwide.
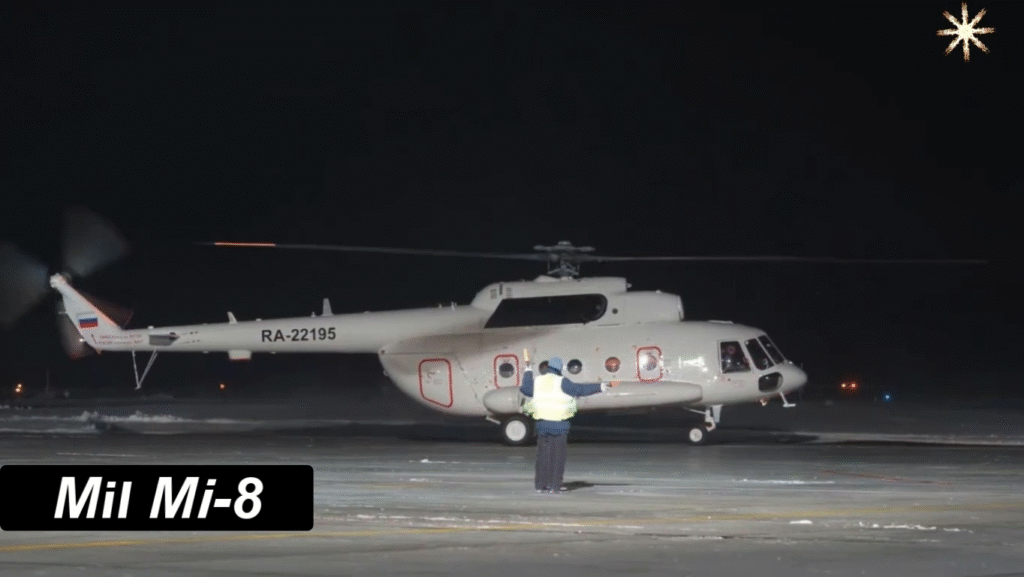


Background and Historical Context
Emerging during the Cold War, the Mi-8 was the Soviet Union’s answer to the growing demand for a multipurpose helicopter that could serve combat, transport, and rescue operations. It evolved from the earlier Mil Mi-4, incorporating twin engines for improved reliability, power, and safety — a major advancement in rotary-wing aviation at the time.
Design Philosophy and Development Goals
The Mi-8 was built around three core principles: simplicity, durability, and versatility. Soviet engineers designed it to perform in extreme climates — from Arctic snowfields to desert sands — while maintaining easy maintenance and low operational costs. This pragmatic approach allowed it to thrive globally, from Eastern Europe to Africa and Asia.
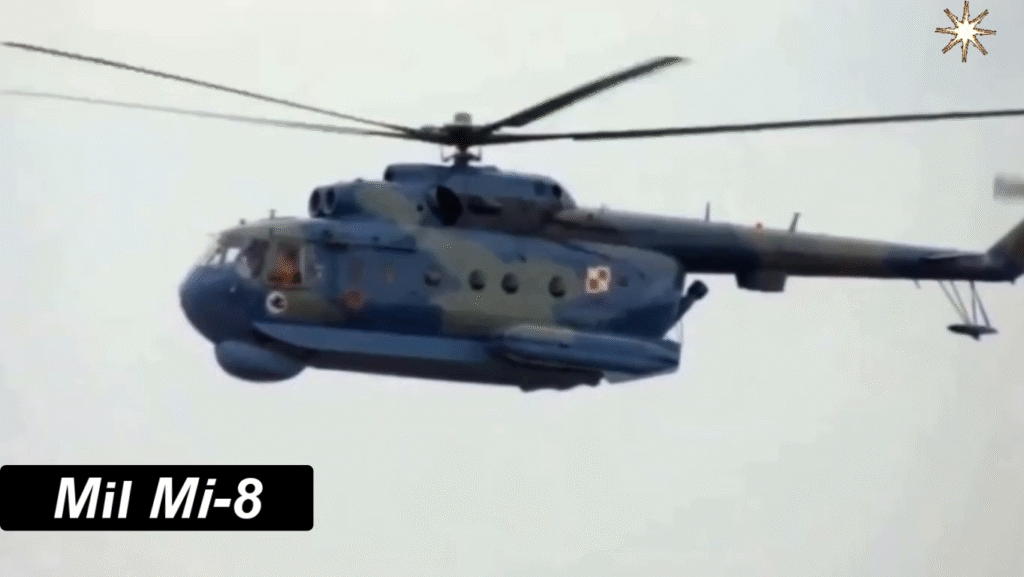

General Information: Overview of the Mil Mi-8 Helicopter
Role and Purpose of the Mi-8
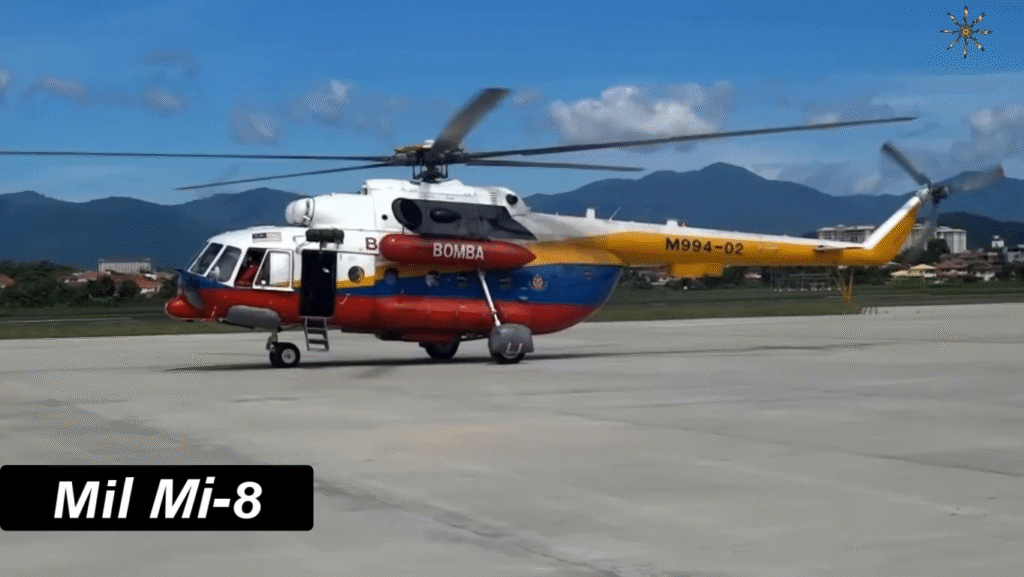
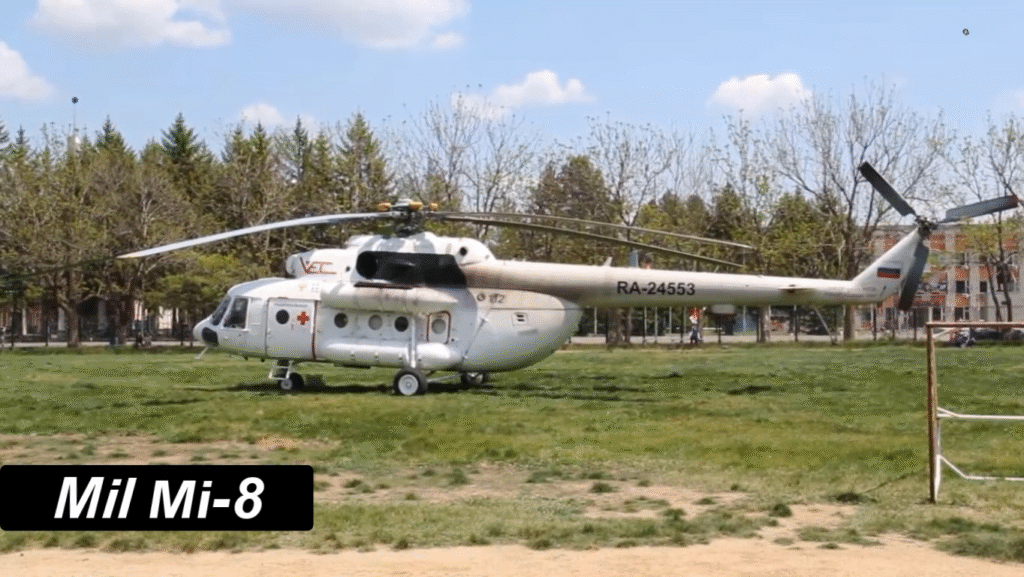
At its core, the Mi-8 is a multi-purpose transport helicopter, capable of carrying troops, cargo, or medical evacuees. Its cabin can accommodate 24 passengers, 12 stretchers, or around 4,000 kg (8,800 lb) of cargo either internally or externally via a sling.
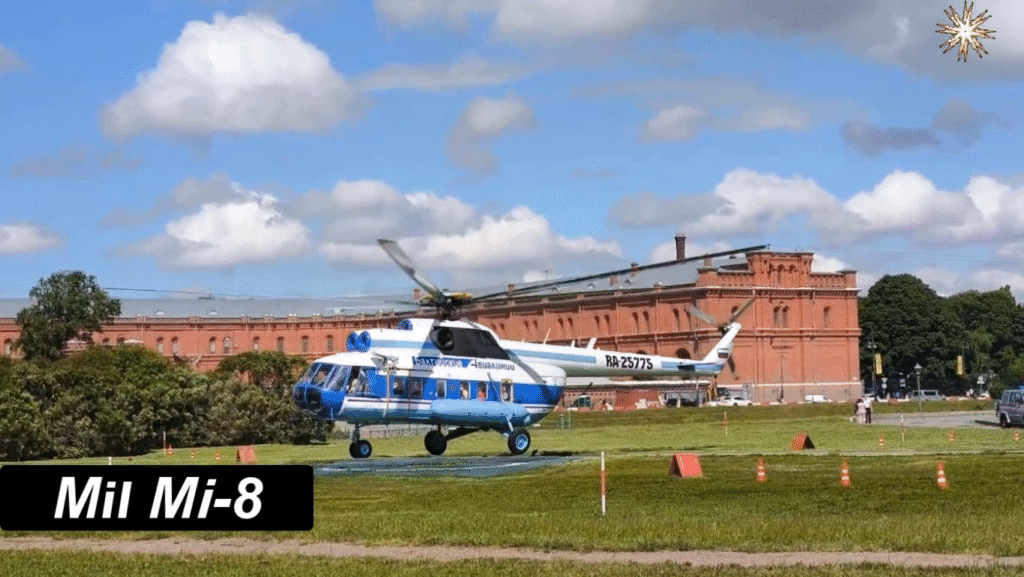
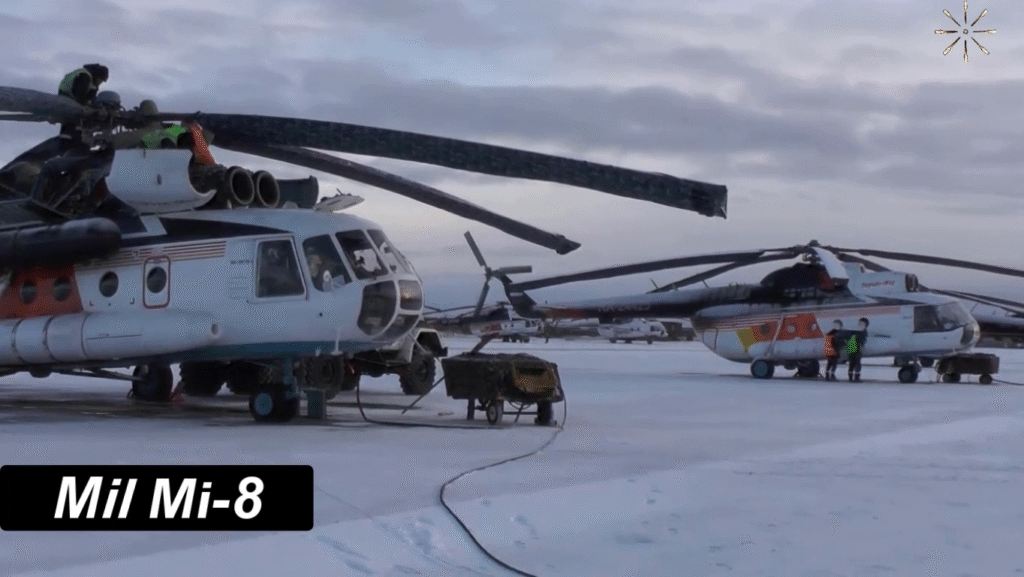
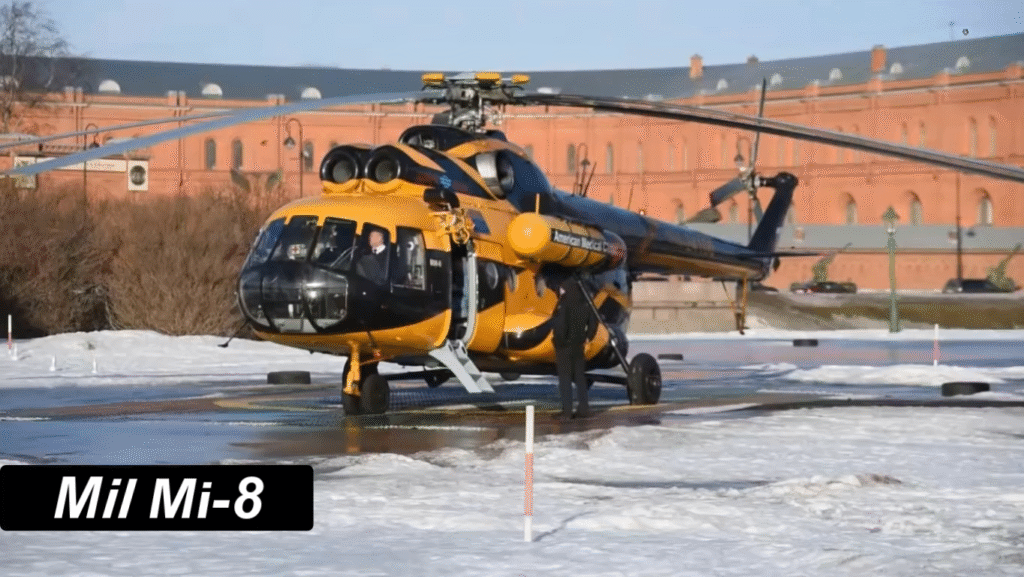
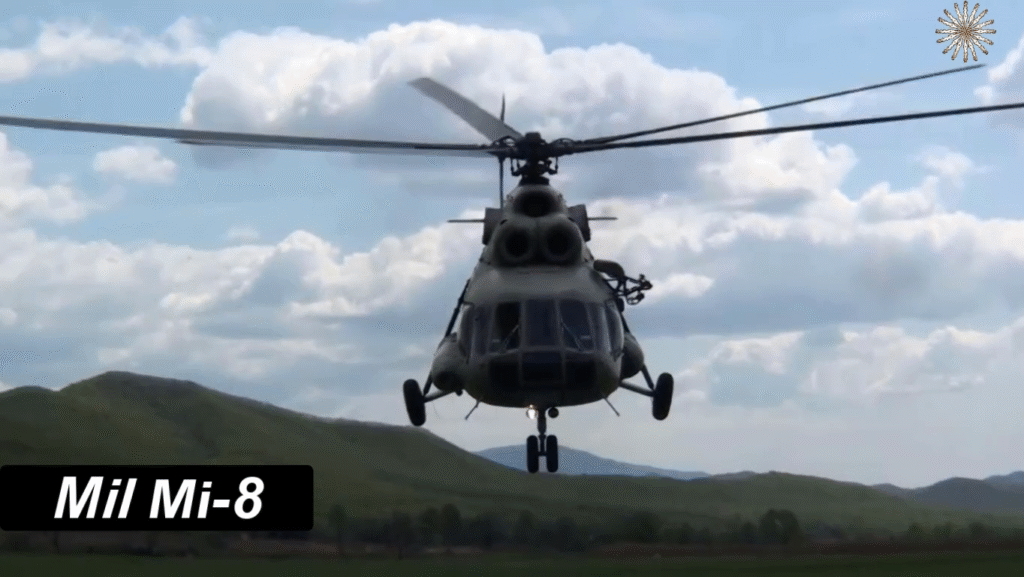





First Flight, Production, and Entry into Service
After its first flight in 1961, mass production began in 1965, and by 1967, it officially joined the Soviet Air Force. Over time, the Mi-8 became one of the most produced helicopters in history, with over 17,000 units built — a testament to its design excellence.
Global Popularity and Production Scale
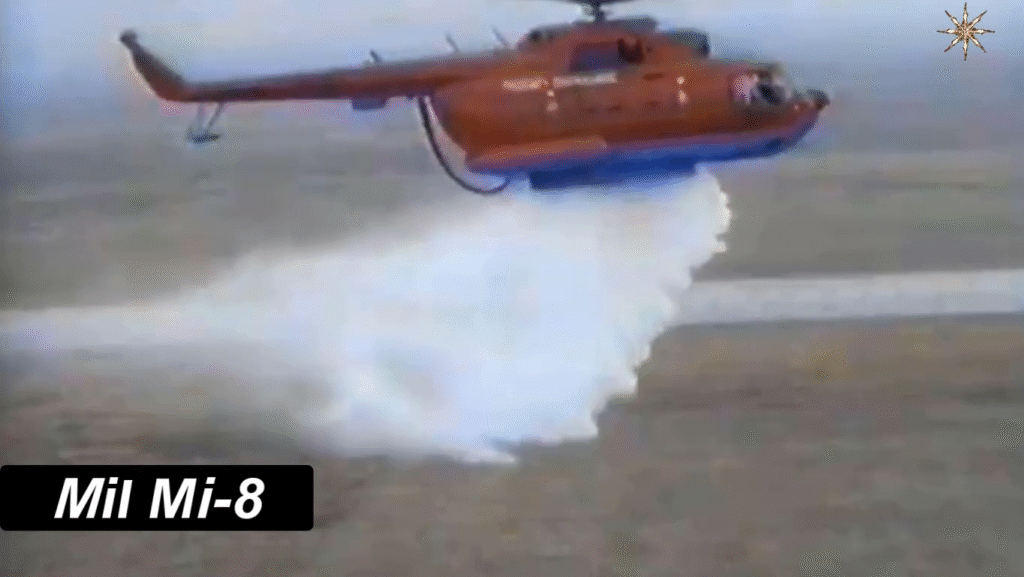
The Mi-8 has served in more than 50 countries, adapted for countless missions — from combat to firefighting. Its reputation for ruggedness and reliability made it indispensable in harsh environments where few aircraft could operate effectively.
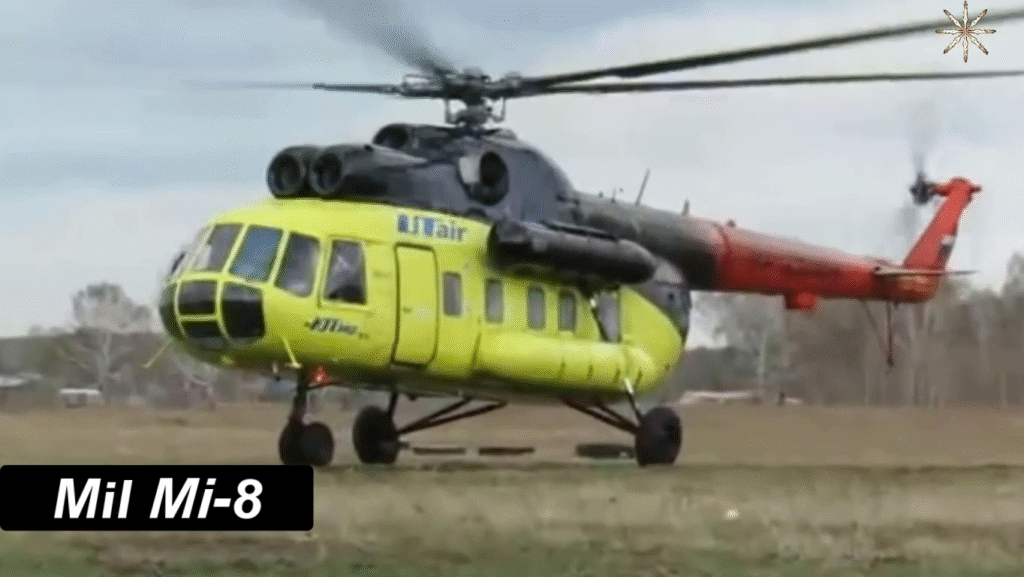
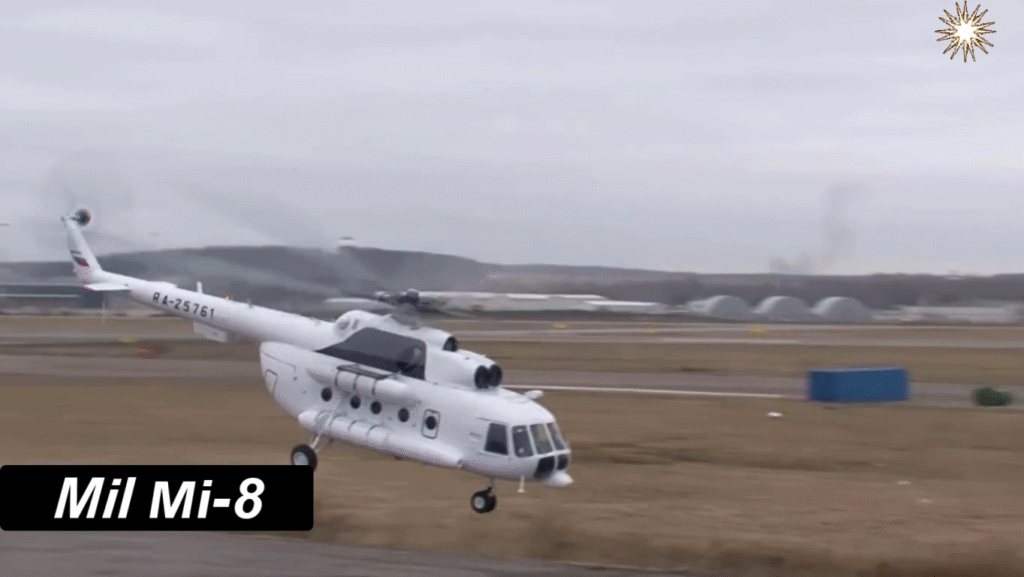
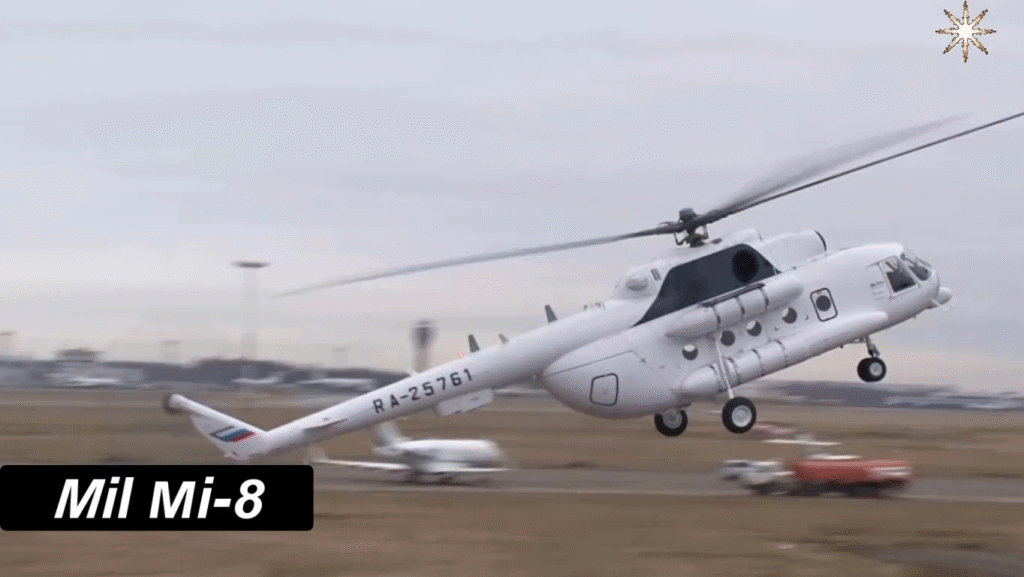
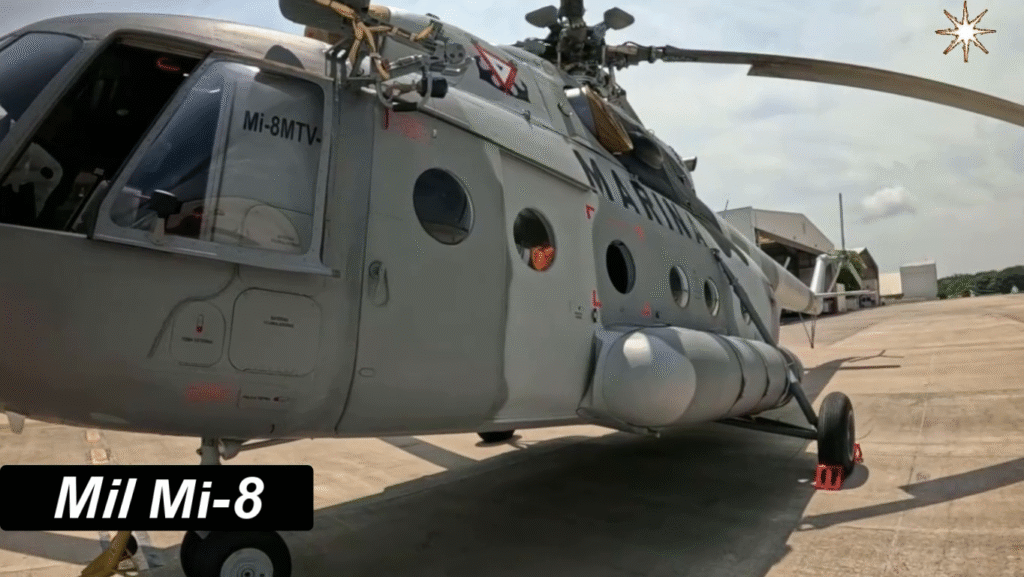
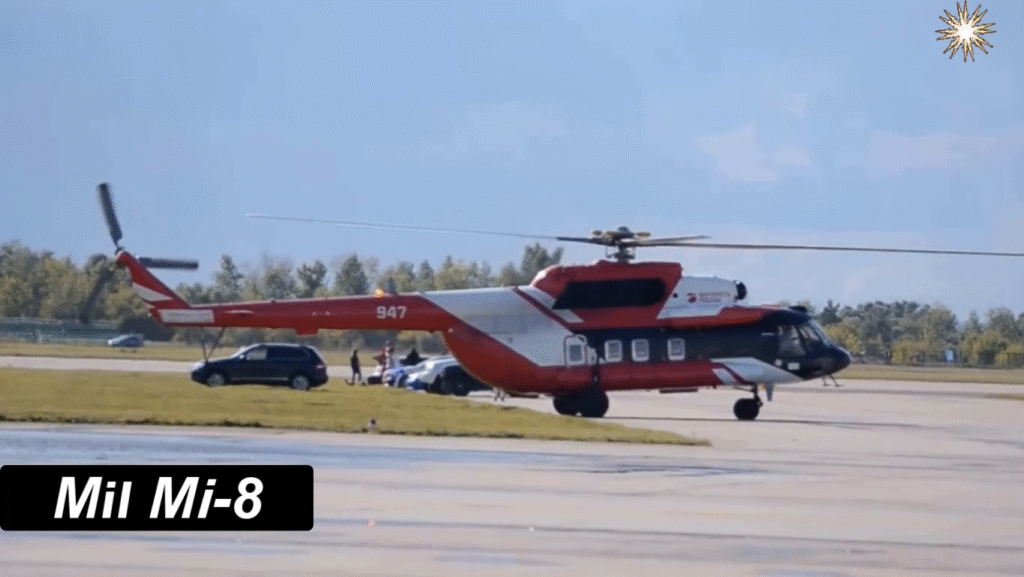
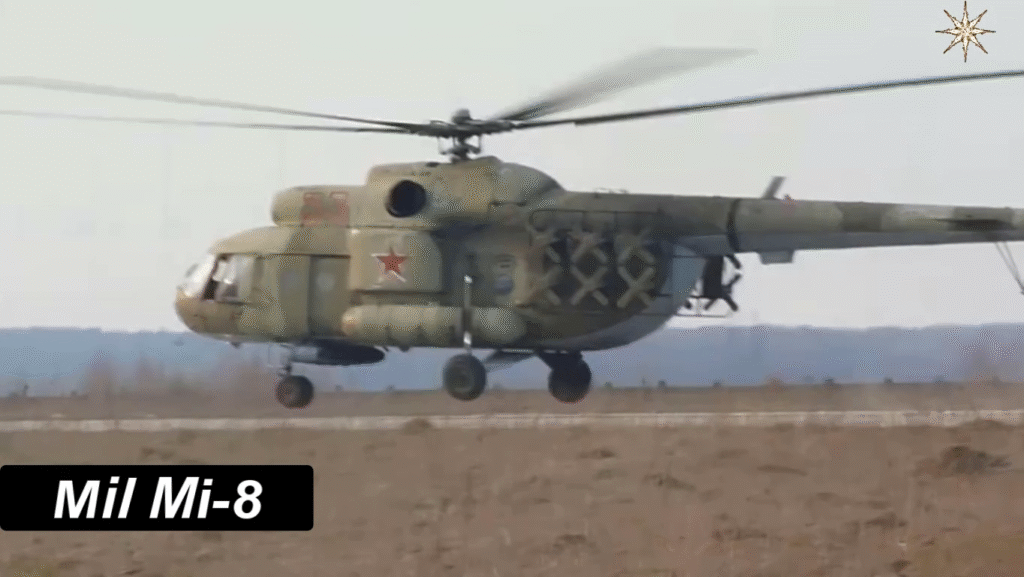







Technical Specifications of the Mil Mi-8 (Mi-8T Variant)
Powerplant and Propulsion System
The Mi-8T variant is powered by two Klimov TV2-117 turboshaft engines, each delivering 1,700 horsepower. This twin-engine configuration not only enhanced lift capacity but also improved operational safety in case of engine failure.
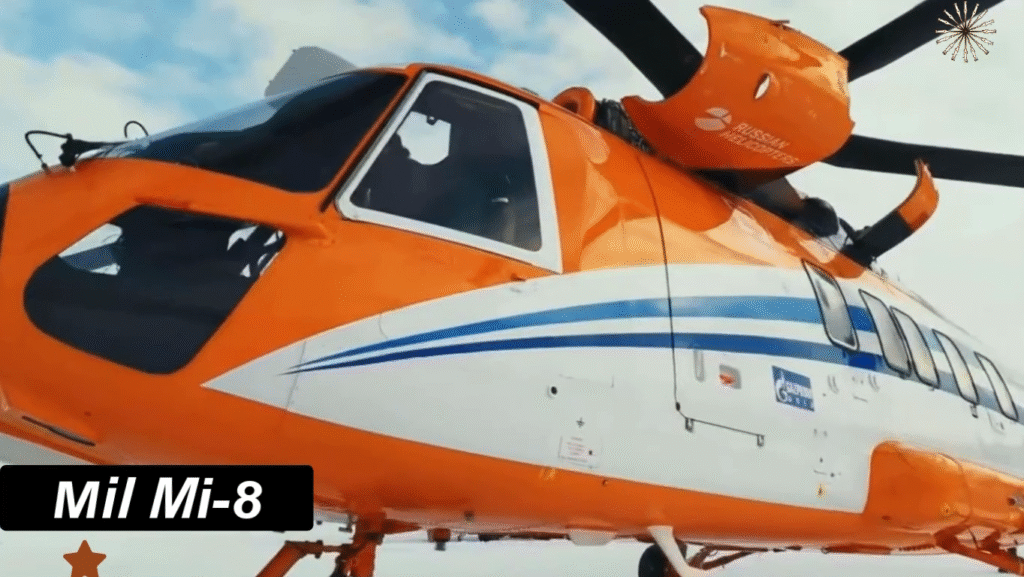
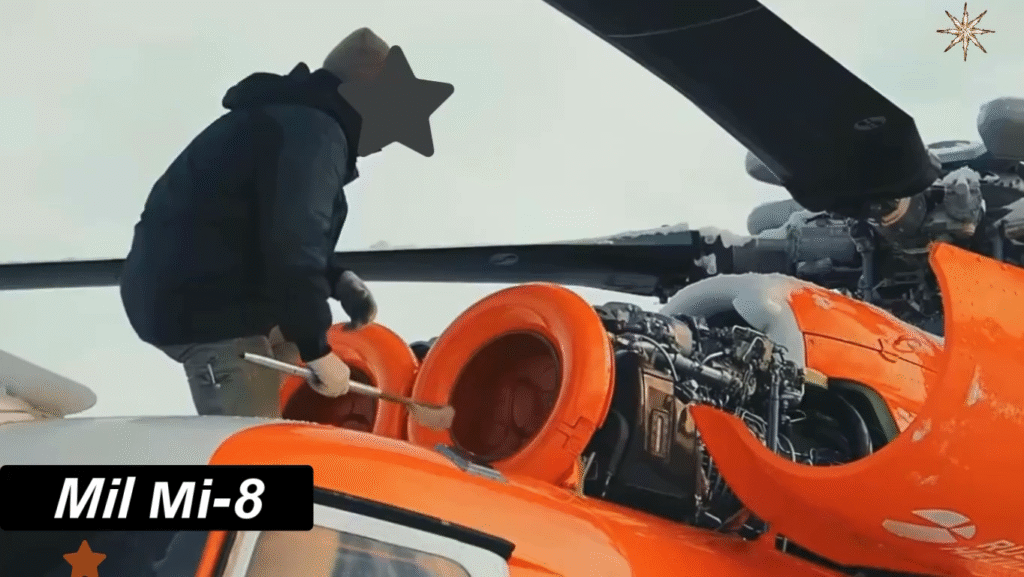


Performance and Flight Characteristics
With a maximum speed of 250 km/h (155 mph) and a range of approximately 450 km (280 mi) — extendable with auxiliary fuel tanks — the Mi-8 provides exceptional endurance for both short and mid-range missions. It can climb to a service ceiling of 4,500 meters (14,750 feet), ideal for mountainous terrain.
Dimensions, Weight, and Capacity
The helicopter has a takeoff weight of 12,000 kg (26,455 lb), allowing it to transport large payloads with ease. Its spacious interior supports versatile configurations for passengers, medical stretchers, or military equipment.
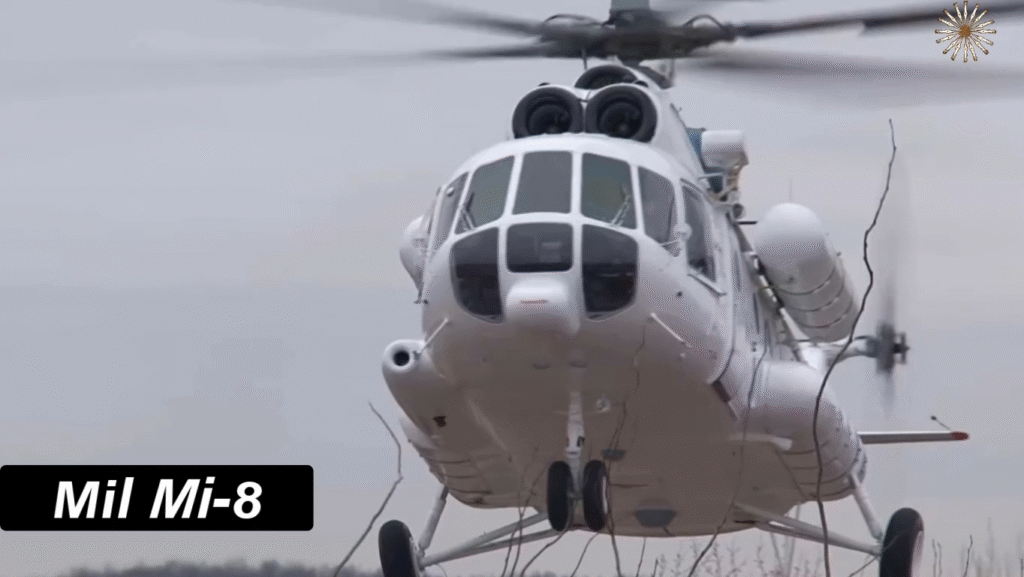
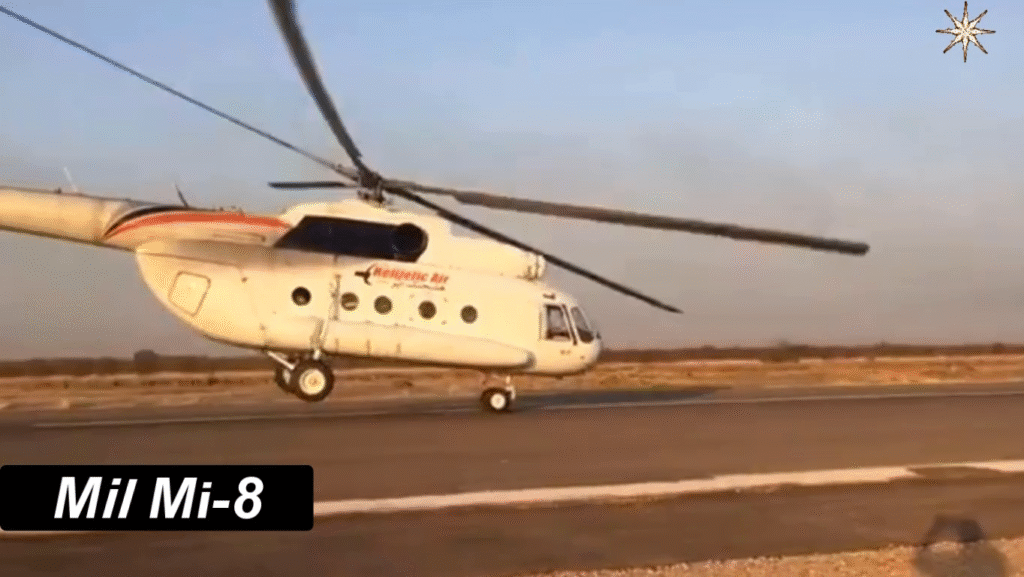
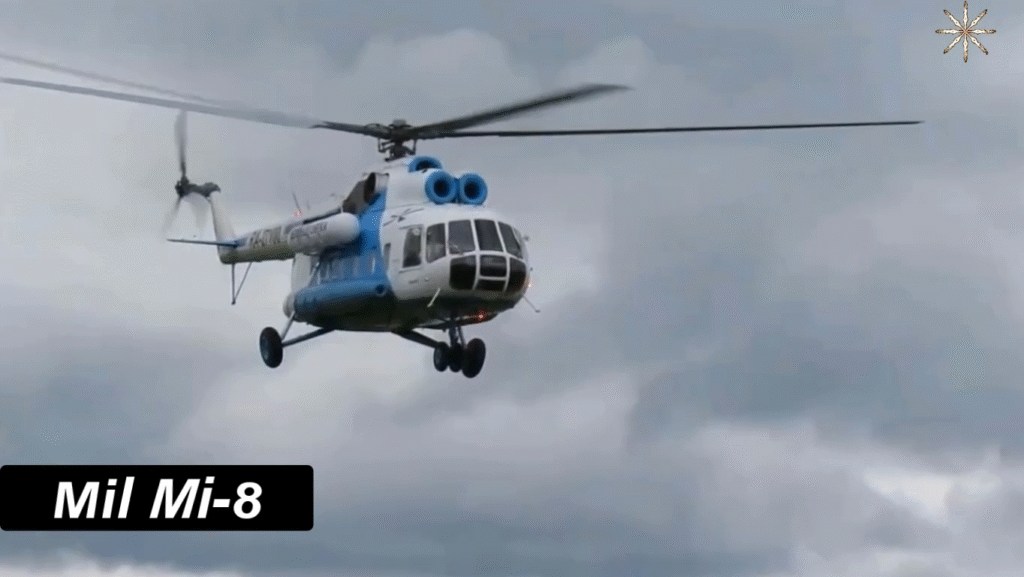
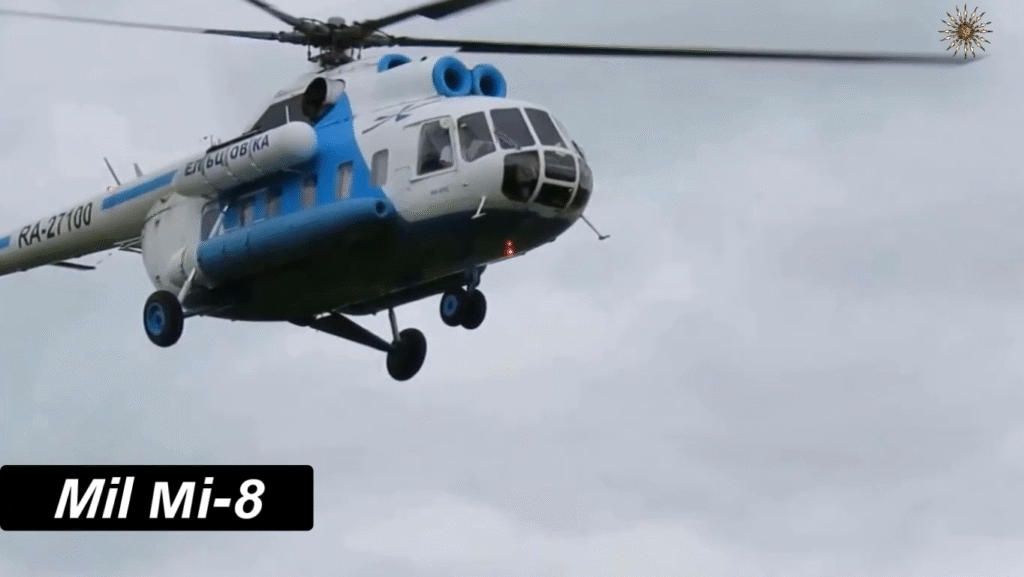
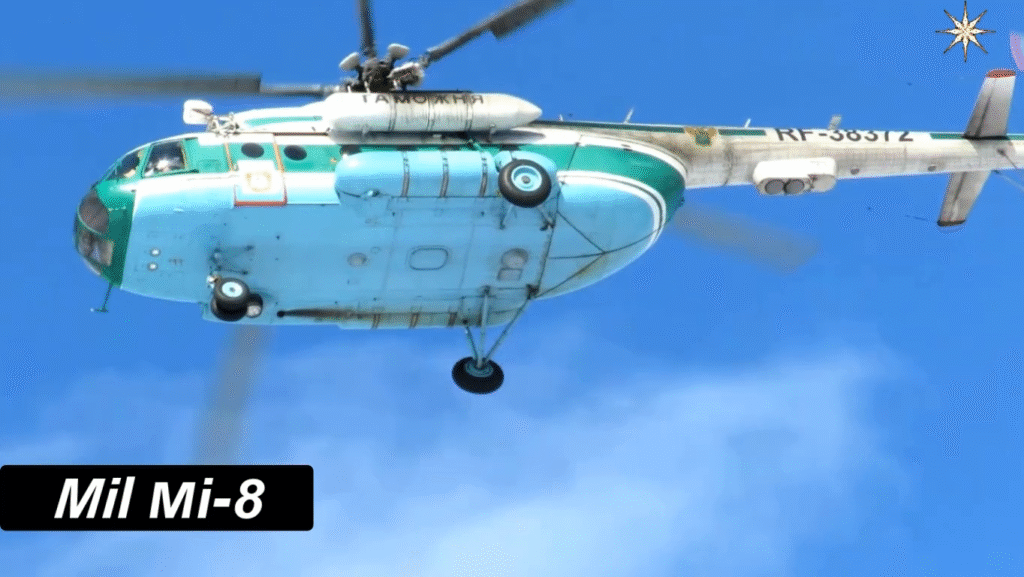






Design and Structure: Engineering Excellence of the Mi-8
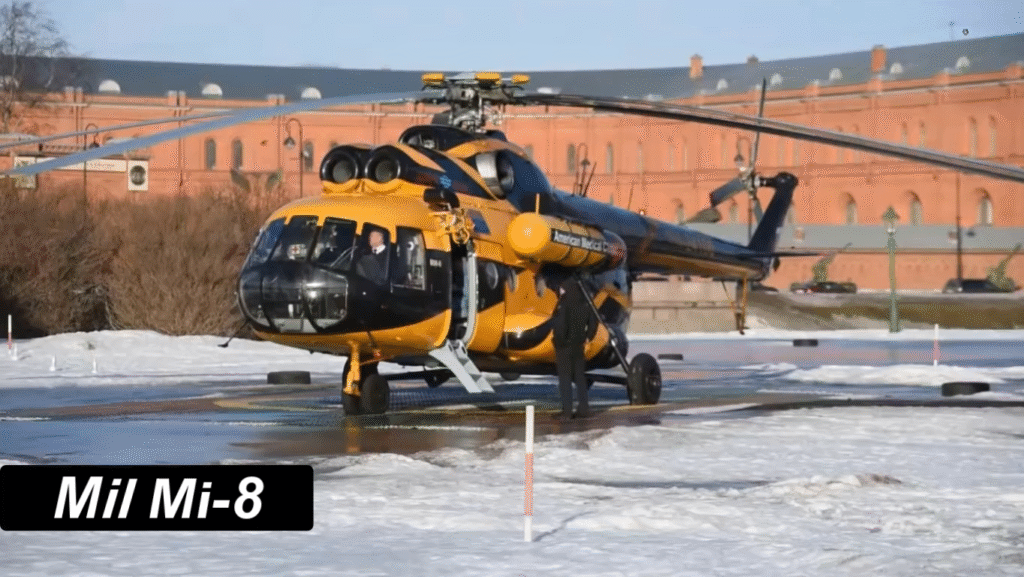
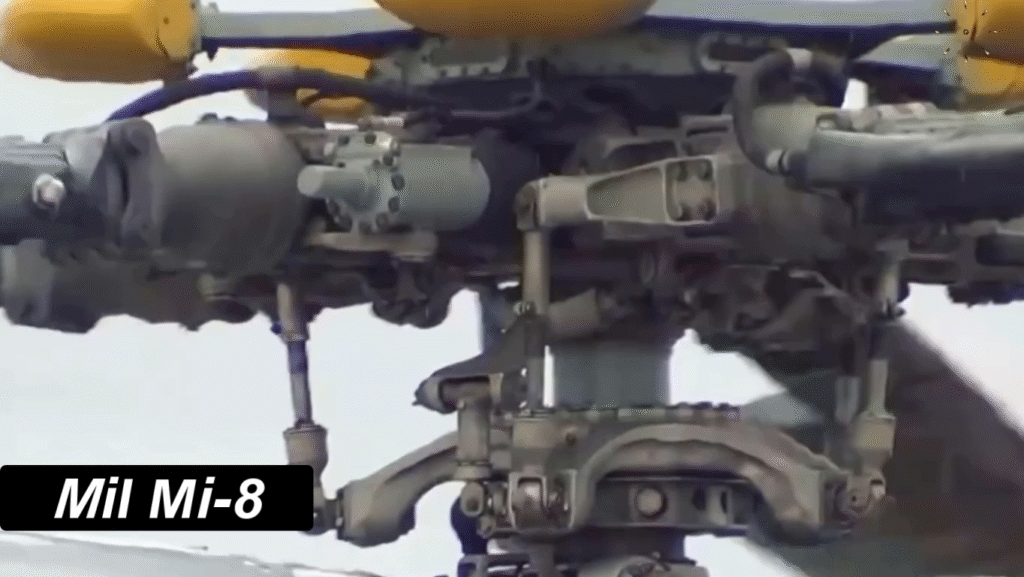
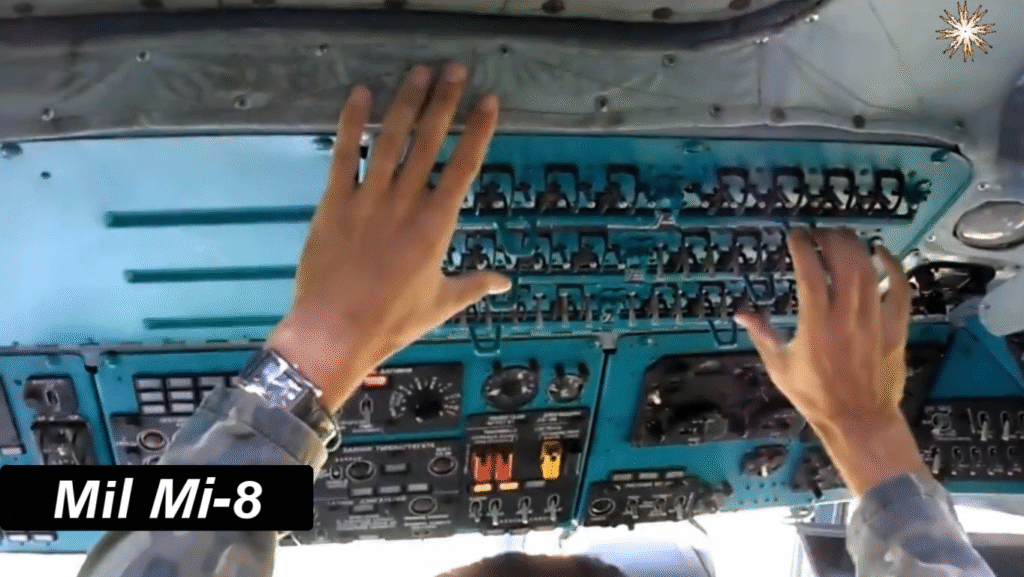
The Mi-8’s robust aluminum fuselage and five-blade main rotor system make it durable and stable, even in turbulent conditions. The aircraft’s three-person crew—pilot, co-pilot, and flight engineer—operates from a cockpit equipped with analog instruments, though modernized variants now include digital avionics.
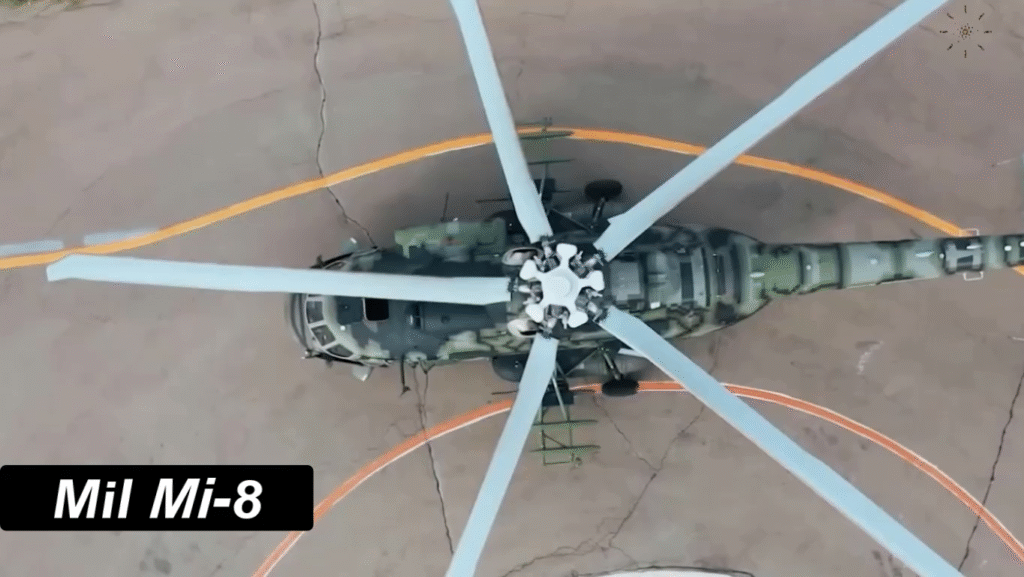





Cargo Handling and Versatility Features
Equipped with a rear clamshell door and a side cargo hatch, loading and unloading are efficient. External cargo slings further extend the helicopter’s utility for construction, rescue, and military logistics.
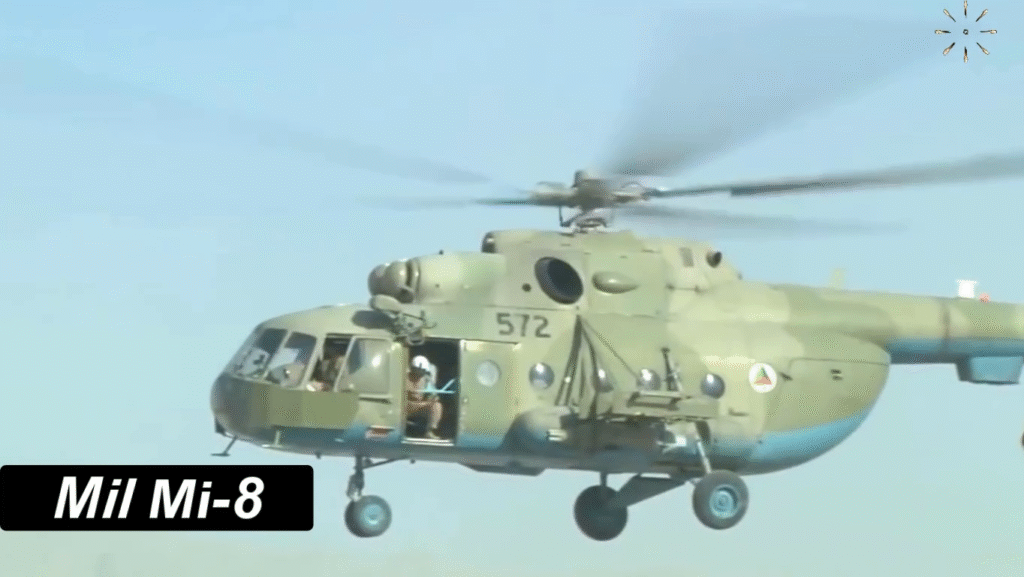

Some Variants of the Mil Mi-8: Evolution and Adaptation
- Mi-8T – Original transport version.
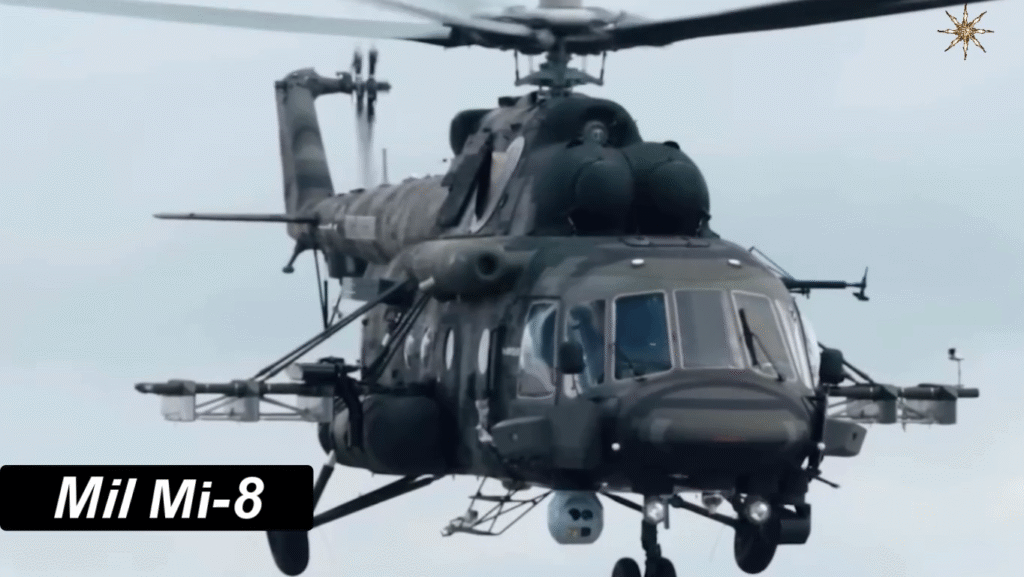
- Mi-8MT / Mi-17 – Upgraded with stronger engines and exported globally.
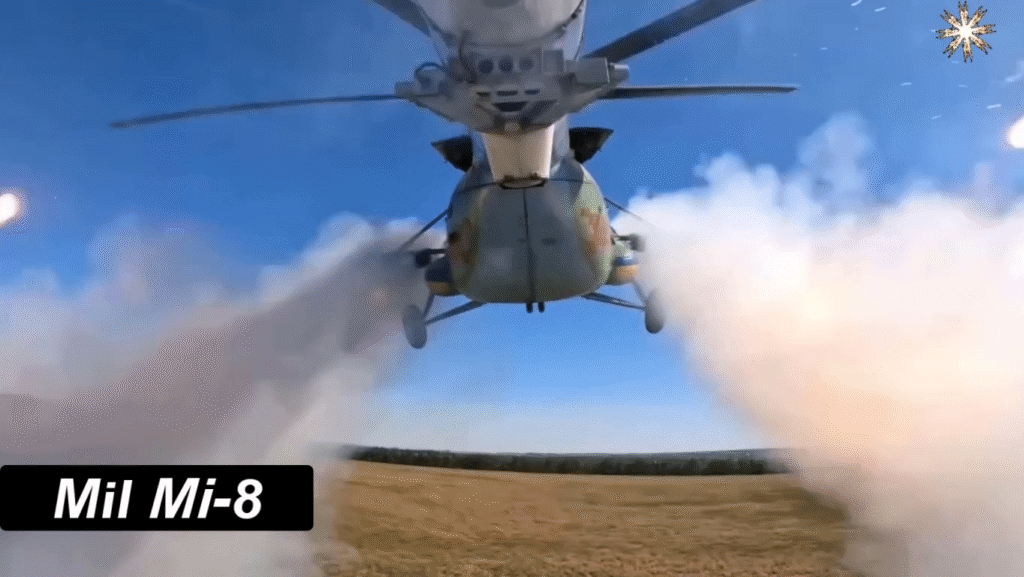
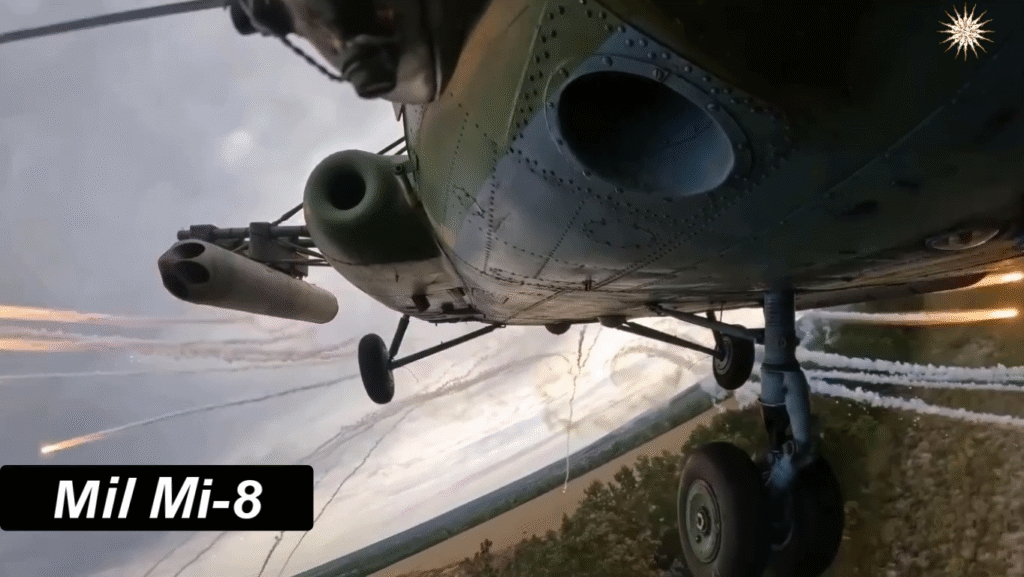
- Mi-8AMTSh – Armed assault model with weapons and armor.
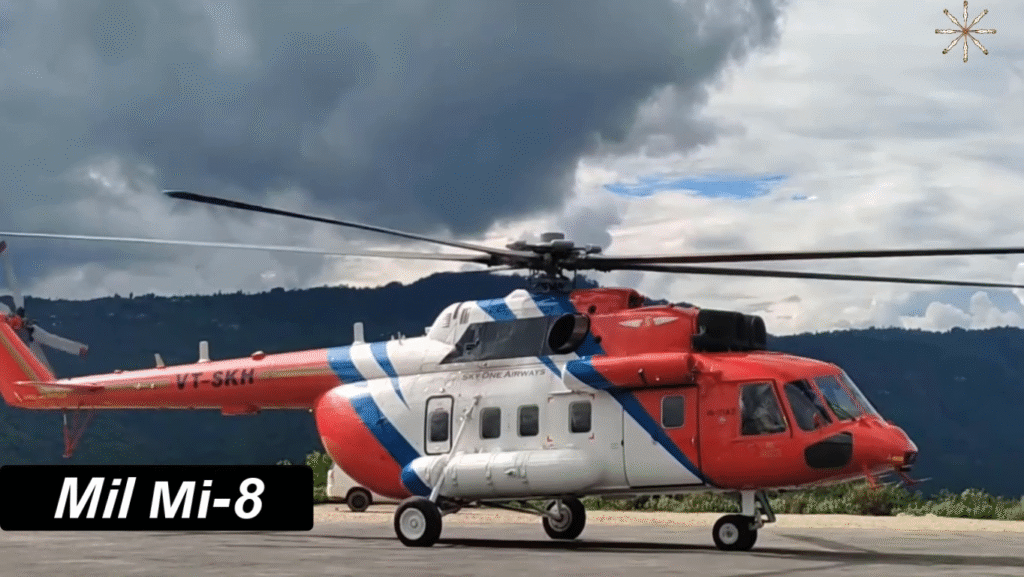
- Mi-8P / Mi-8S – Passenger and VIP versions for civilian use.
Each variant reflects adaptability, proving the Mi-8’s timeless design can evolve with changing mission requirements.
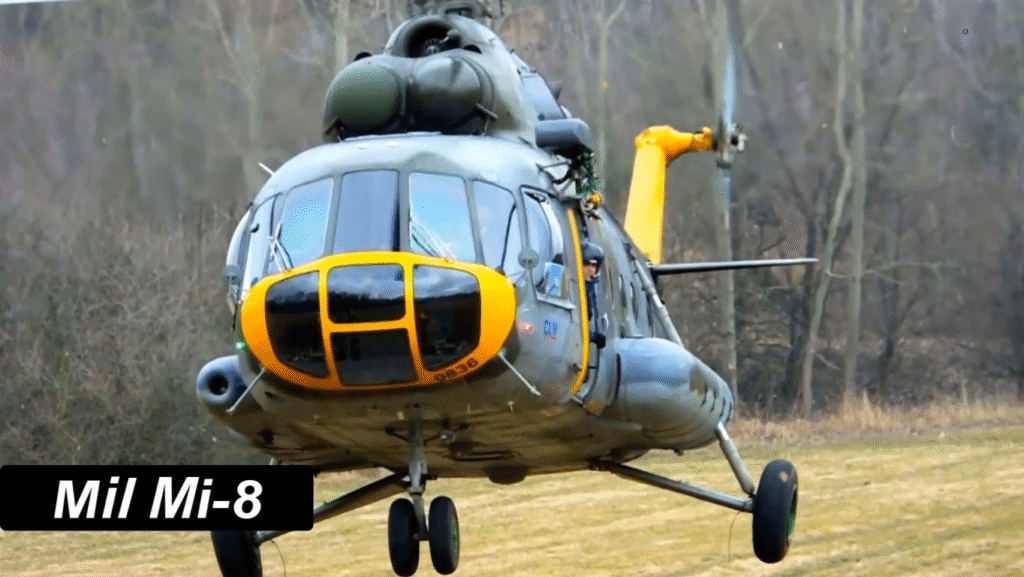
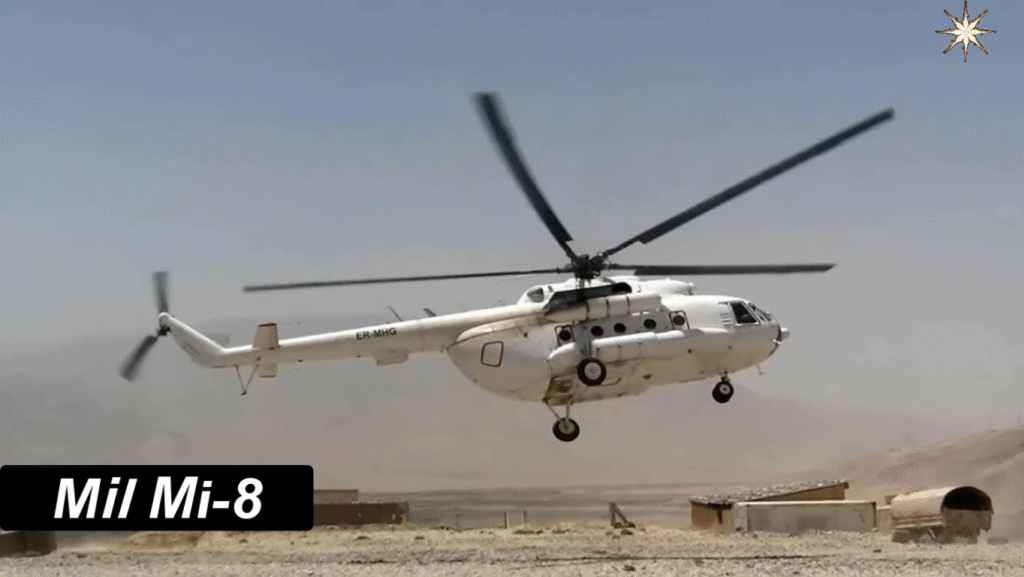
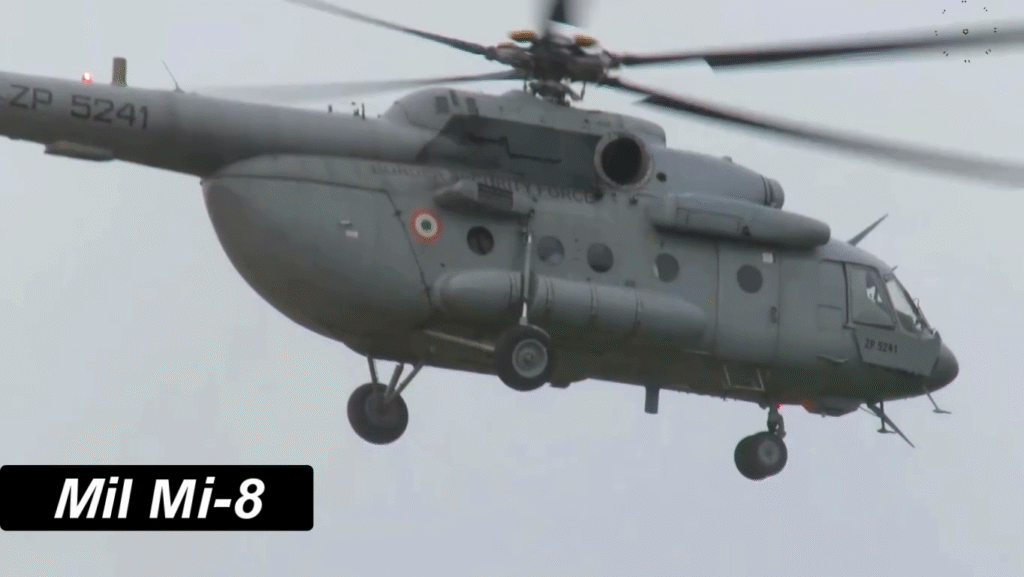
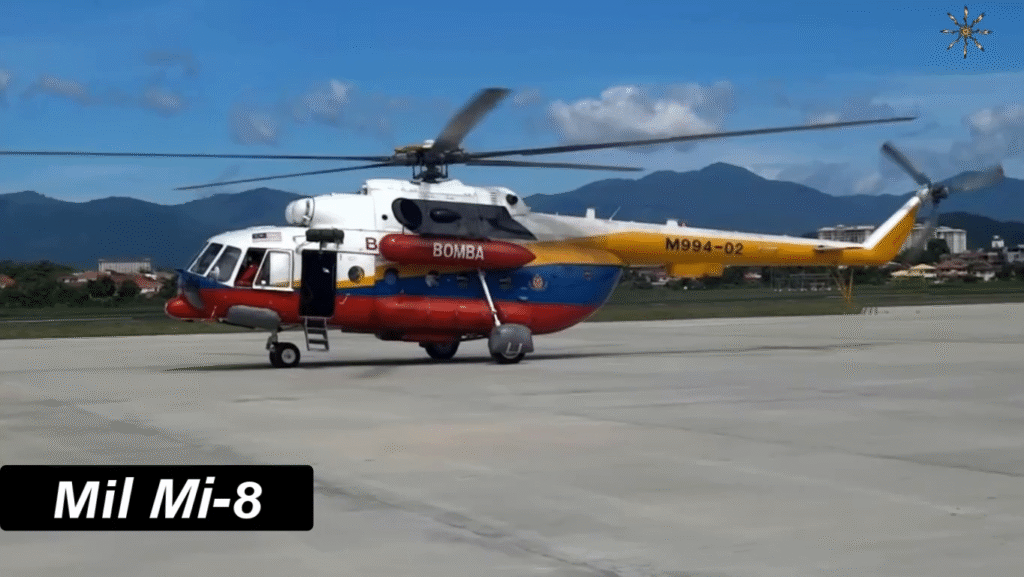
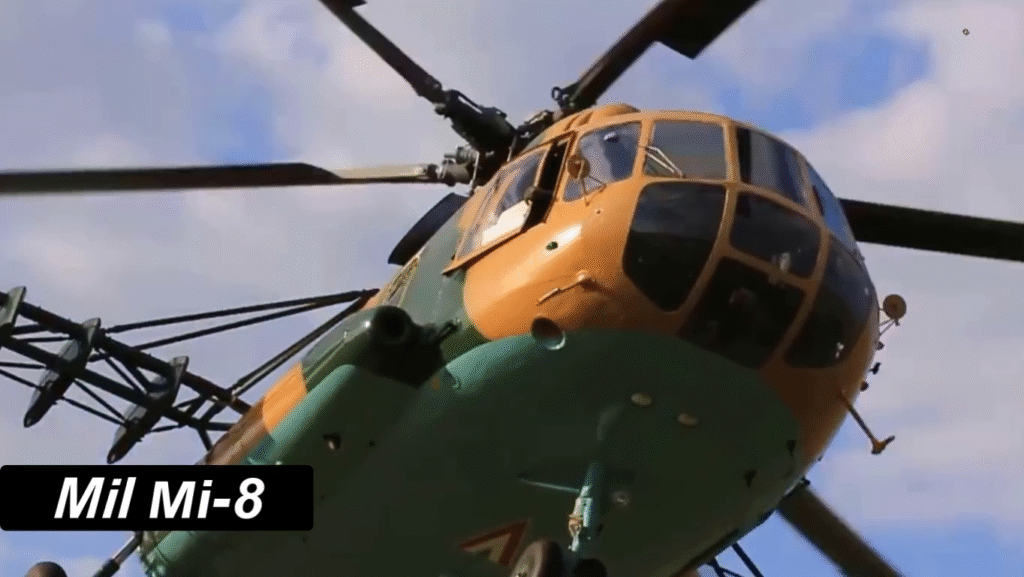








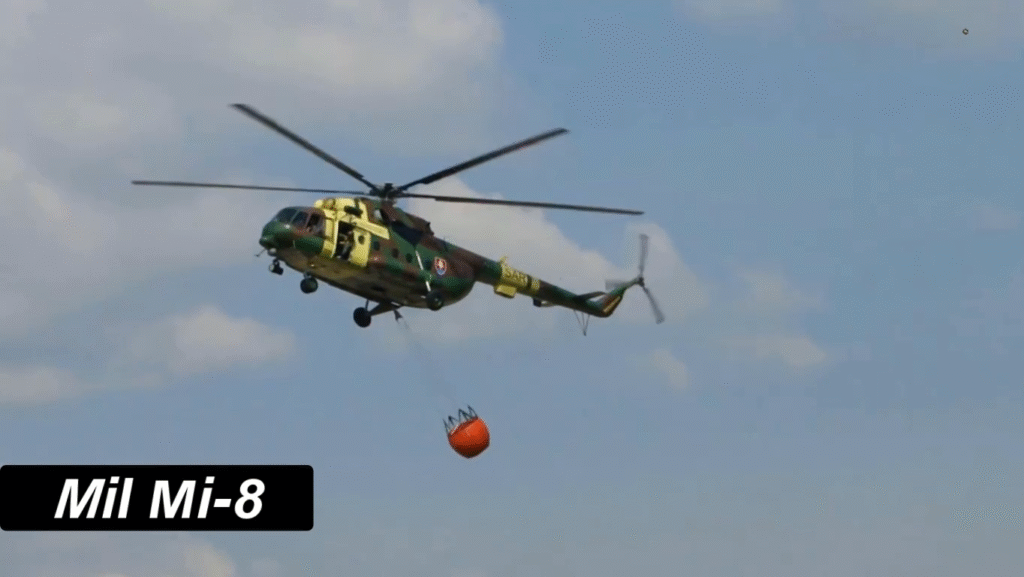
Operational Roles and Global Usage
From troop deployment to disaster relief, the Mi-8 performs a multitude of roles:
- Military: Transport, medevac, and gunship operations.
- Civilian: Firefighting, search and rescue, and aerial construction.
- Peacekeeping: Used by the UN for humanitarian and emergency missions.
Notable Missions and Historical Impact
The Mi-8 saw extensive use in Afghanistan (1979–1989), Africa, and Eastern Europe, where its ability to operate in high-altitude and rugged terrain proved invaluable. It has also been used in numerous disaster relief operations, including earthquake and flood evacuations worldwide.
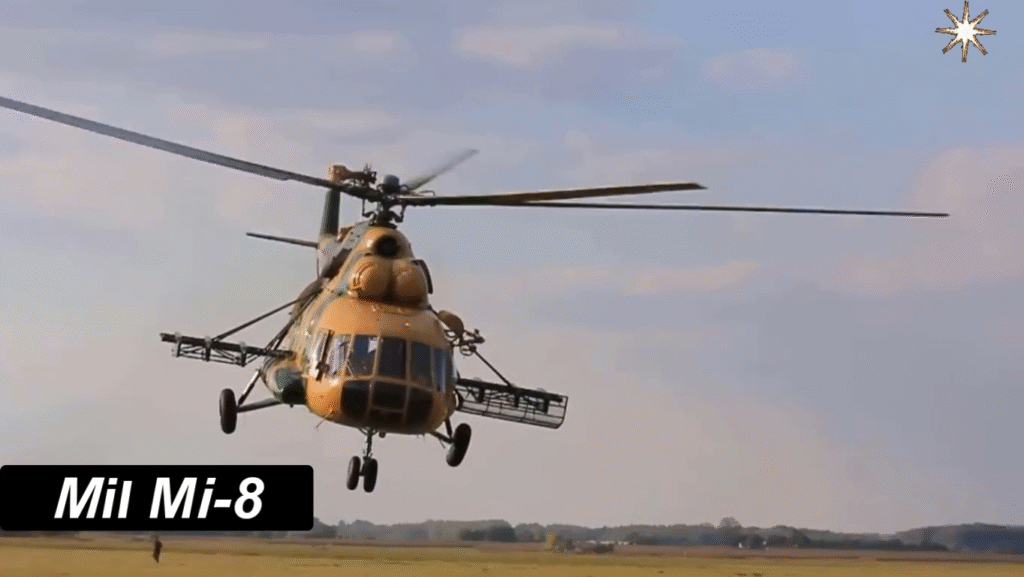
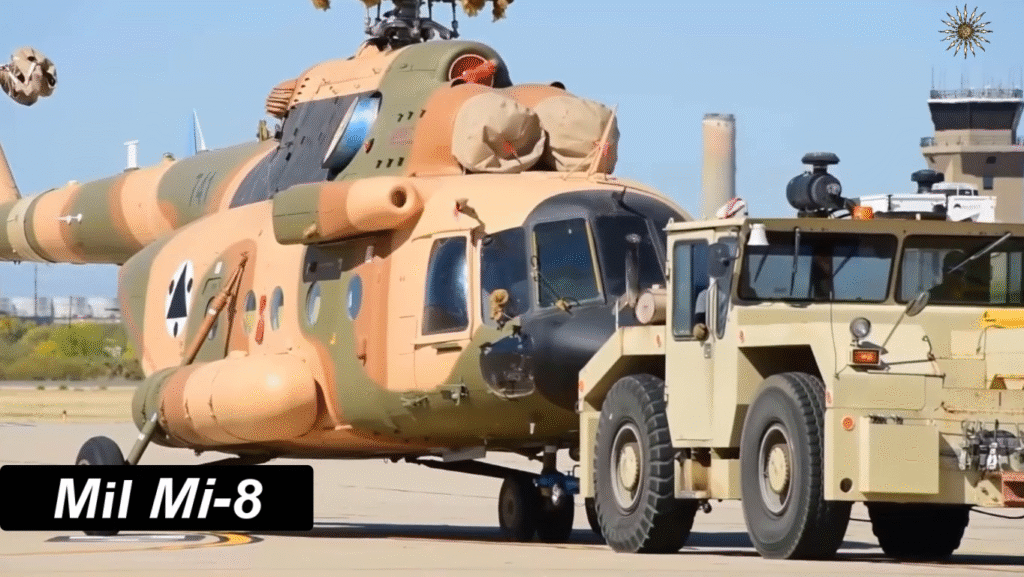
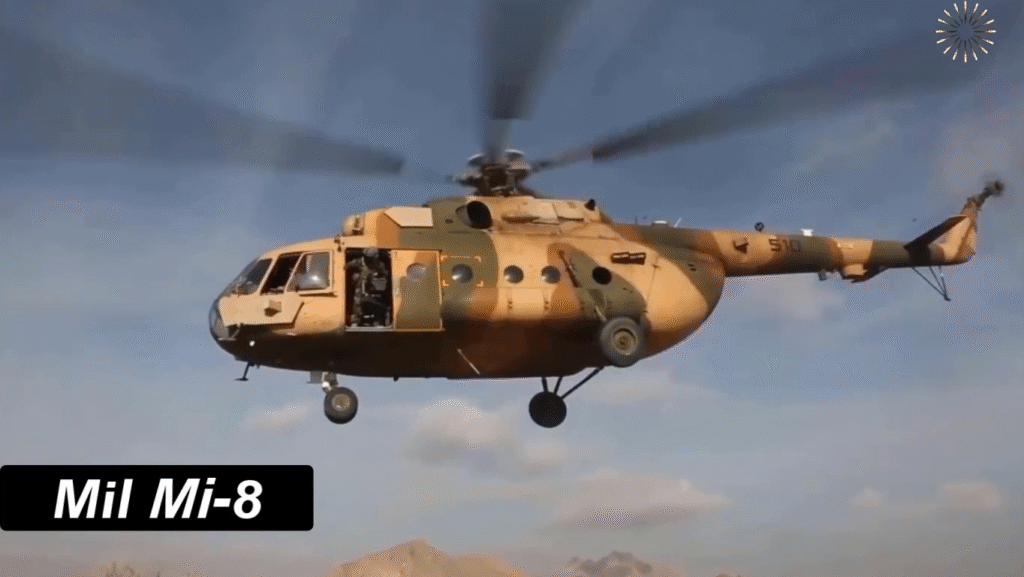
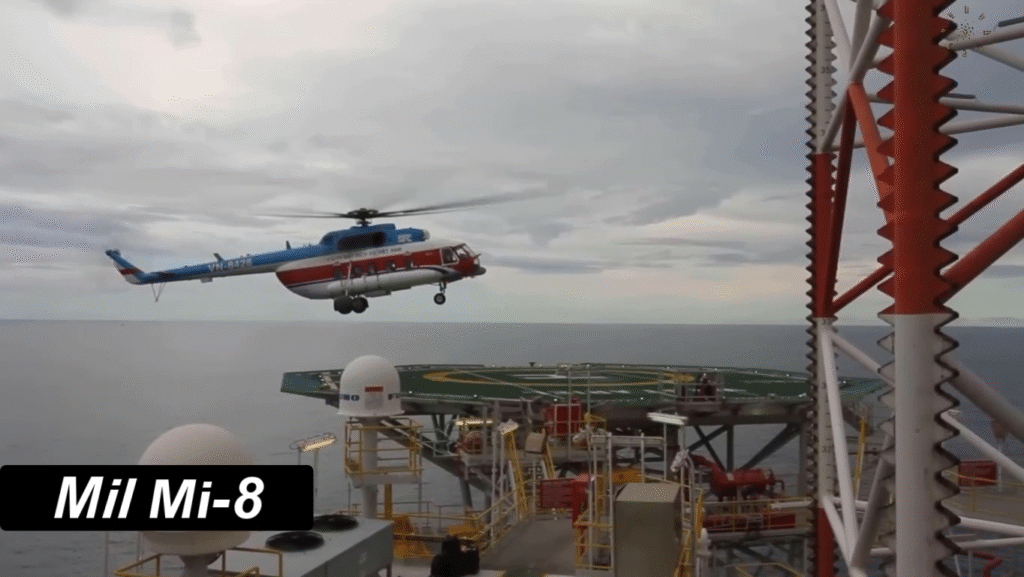
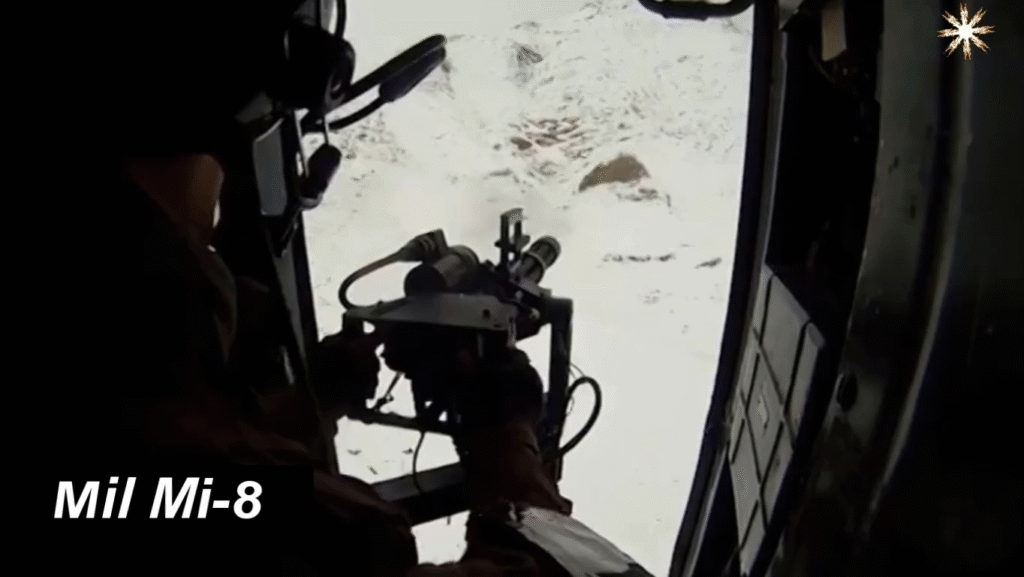
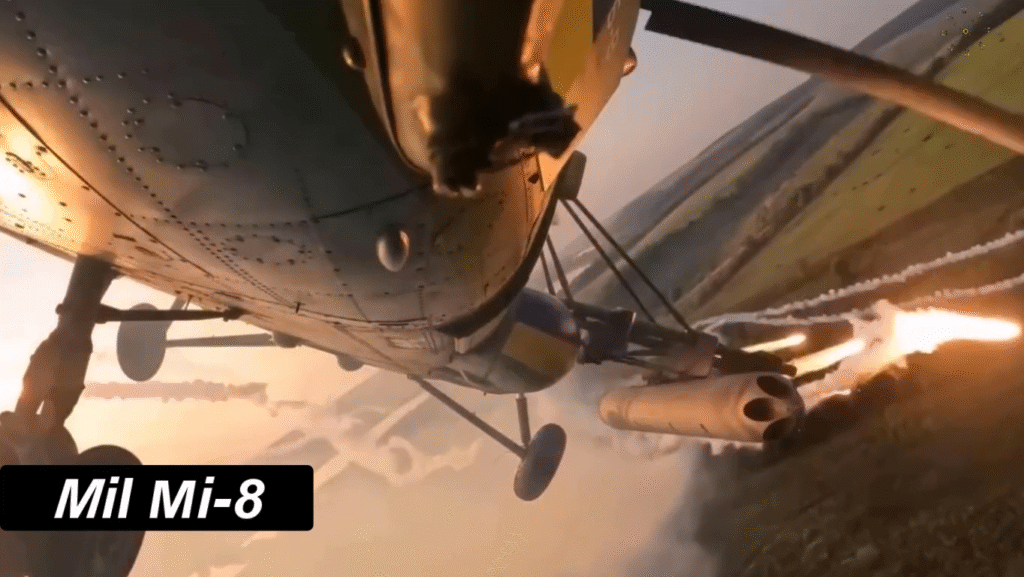
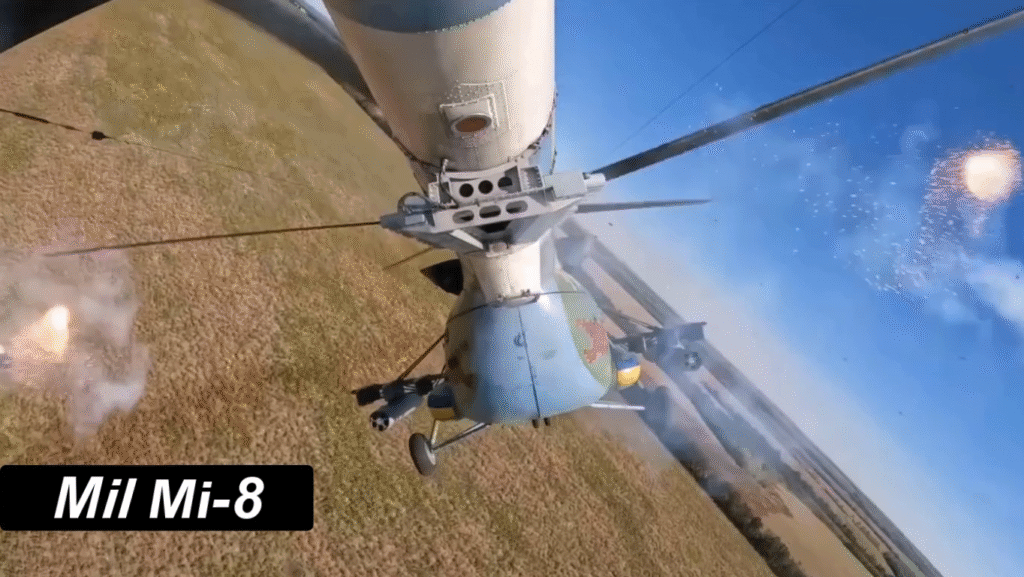











Modern Upgrades and Continued Service
Even after six decades, the Mi-8 remains in active production and service. Newer variants feature glass cockpits, GPS systems, advanced radar, and improved Klimov engines. Many air forces continue to modernize their fleets rather than replace them outright.
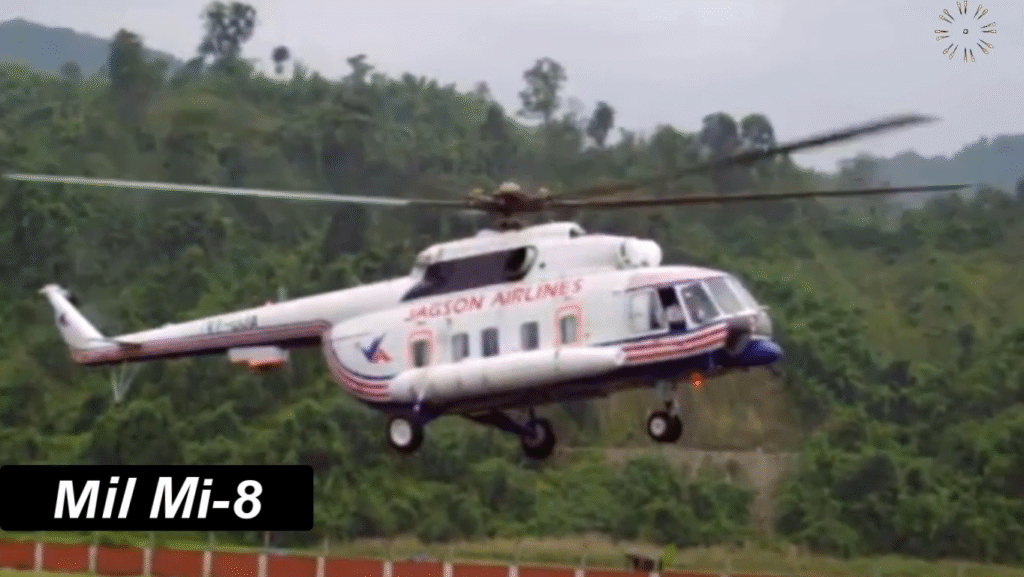

FAQs About the Mil Mi-8 Helicopter
1. How many Mil Mi-8 helicopters were built?
Over 17,000 units have been produced since the 1960s.
2. What makes the Mi-8 so popular?
Its versatility, ease of maintenance, and ability to perform in extreme conditions make it one of the most dependable helicopters ever made.
3. What countries use the Mi-8?
It serves in over 50 countries, including Russia, India, China, and Ukraine.
4. What’s the difference between Mi-8 and Mi-17?
The Mi-17 is an upgraded version with more powerful engines and export-friendly avionics.
5. Can the Mi-8 carry weapons?
Yes, certain variants like the Mi-8AMTSh are equipped with rockets, guns, and defensive systems.
6. Is the Mi-8 still in production?
Yes, modernized versions of the Mi-8 and Mi-17 are still being produced by Russian Helicopters.
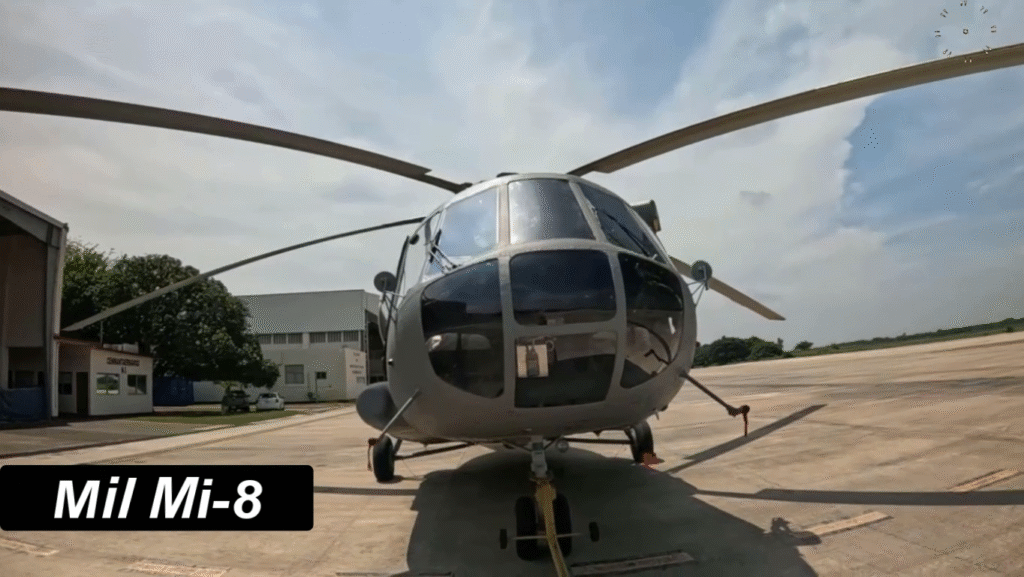

Conclusion: Why the Mil Mi-8 Remains a Timeless Icon
The Mil Mi-8 stands as a symbol of engineering excellence and enduring reliability. From warzones to humanitarian missions, this Soviet masterpiece has proven its worth for more than six decades. Its influence continues through modern variants and global operators, marking it as one of the greatest helicopters ever built.